Top 5 reasons to automate controls?


What are Application Controls?
Application controls apply to the business processes they support. These controls are designed within the application to prevent or detect unauthorized transactions. When combined with manual controls, as necessary, application controls ensure completeness, accuracy, authorization and validity of processing transactions. Control objectives can be supported with automated application controls. They are the most effective in integrated ERP environments, such as SAP, PeopleSoft, Oracle E-Business Suite, J D Edwards and others.
Examples of application controls
The following are examples of application controls:
- Orders are processed only within approved customer credit limits.
- Orders are approved by management as to prices and terms of sale.
- Purchase orders are placed only for approved requisitions.
- Purchase orders are accurately entered.
- All purchase orders issued are input and processed.
- All recorded production costs are consistent with actual direct and indirect expenses associated with production.
- All direct and indirect expenses associated with production are recorded as production costs.
Risk Assessment
The IT organization has an entity and activity level risk assessment framework, which is used periodically to assess information risk to achieving business objectives. Management’s risk assessment framework focuses on the examination of the essential elements of risk and the cause and effect relationship among them. A risk assessment framework exists and considers the risk assessment probability and likelihood of threats. The IT organization’s risk assessment framework measures the impact of risks according to qualitative and quantitative criteria. The IT organization’s risk assessment framework is designed to support cost-effective controls to mitigate exposure to risks on a continuing basis, including risk avoidance, mitigation or acceptance. A comprehensive security assessment is performed for critical systems and locations based on their relative priority.
Control Activities
An organization has and does the following:
- A system development life cycle methodology that considers security, availability and processing integrity requirements of the organization. This ensures that information systems are designed to include application controls that support complete, accurate, authorized and valid transaction processing.
- An acquisition and planning process that aligns with its overall strategic direction.
- Acquires software in accordance with its acquisition and planning process.
- Procedures ensure that system software is installed and maintained in accordance with the organization’s requirements.
- Procedures ensure that system software changes are controlled in line with the organization’s change management procedures.
- Ensures that the implementation of system software do not jeopardize the security of the data.
Control Monitoring
Changes to IT systems and applications are performed and designed to meet the expectations of users.
IT management monitors its delivery of services to identify shortfalls and responds with actionable plans to improve.
IT management monitors the effectiveness of internal controls monitoring in the normal course of operations through management and supervisory activities, comparisons and benchmarks.
Serious deviations in the operation of internal control, Monitoring including major security, availability and processing integrity events, are reported to senior management.
Internal control assessments are performed periodically, using Monitoring self-assessment or independent audit, to examine whether internal controls are operating satisfactorily.
Achieving regulatory compliance requires more than IT policies and process documentation.
Effective application audit planning requires mapping controls over application test environments, audit units and significant business processes based on risk likelihood and impact to thousands of functions and activities accessible through many roles, menus and functions.
Detecting users that have unauthorized access to one or more critical business functions such as purchase to pay requires business analytics based on application control rules.
Compensating controls are needed for certain users and transactions where business constraints require exceptions.
Remediation effort requires strong collaboration among Audit, IT and Business stakeholders to reconfigure security, reassign users, prevent configuration changes, monitor transaction thresholds.
ERP Access Provisioning and Configurations must be approved in “real time” to keep up with business needs.
Top 5 Reasons to Automate Controls
Reason 5: Build an Effective Test Plan
Scope application control rules based on IT/Business Risk Likelihood and Impact.
Create application test environment based on a central Master Control Content Library.
Maintains Change Controls over Test Plans to manage changes in application environments.
Reason 4: Detect Control Violations Accurately
Remove false-positives e.g. view-only, hidden or excluded functions.
Exclude control violations where business constraints require “waivers”. Track exception justifications and test compensating controls.
Analyse direct violations within user/role and indirect violations across multiple roles assigned to user.
Reason 3: Faster Remediation Time to Reduce Business Risk
Document and assign remediation tasks to Application and Process Owners.
Perform “what-if” analysis to identify business impact of control operation.
Promote successfully tested application controls to production application environment without error prone manual entries.
Reason 2: Achieve Sustainable Compliance with Preventive Monitoring
Identify Control Violations based on pre-defined IT Policies to prevent Segregation of Duties Violations, Unapproved Configuration Changes and Erroneous Transactions.
Improve Application Change Management Process through electronic approval workflow.
Restrict Access to Sensitive Data.
Reason 1: Reduce Auditing Time and Expense
Reduce Internal and External Application Testing effort by auditing changes to Application Baseline.
Improve Detection to Remediation Cycle through electronic workflow management of control violations.
Reduce Cost of Compliance by replacing manual detection, remediation and prevention activities with streamlined and automated processes.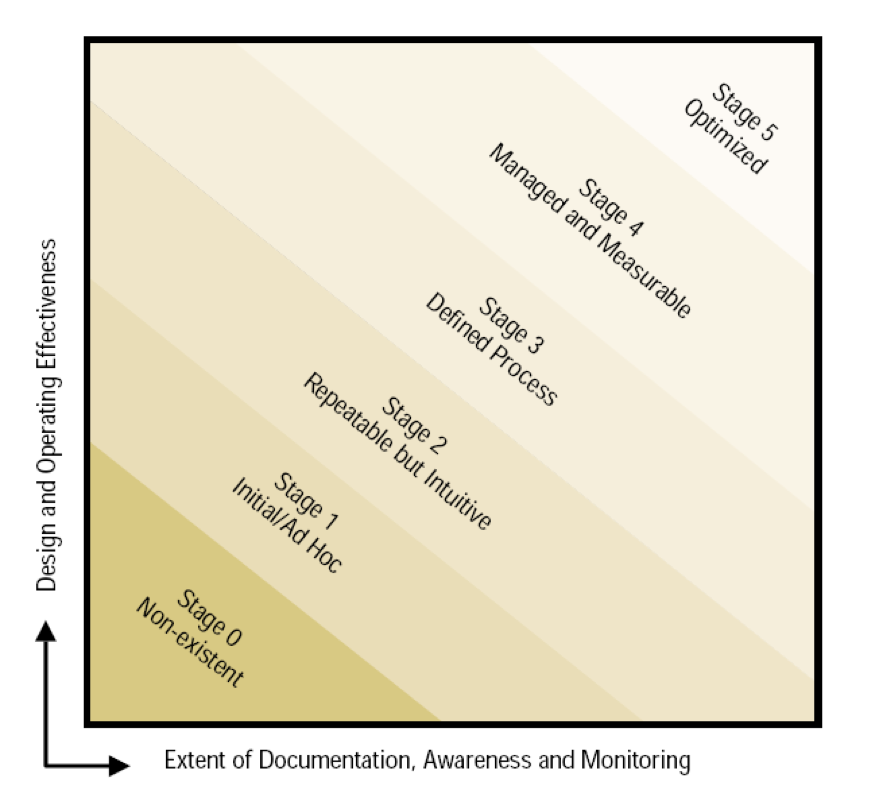
Stages of Control Reliability
Automation Approach
Define: Define Audit Units, Application Environments, and Controls in-scope for Audit Testing
Detect: Analyse Control Violations based on risk, impact. Eliminate false-positives, exceptions
Remediate: Resolve Role, Menu, and Function violations
Prevent: Monitor Application Controls and notify violations in real-time
Predict: Monitor Application Change Management process for future violations

